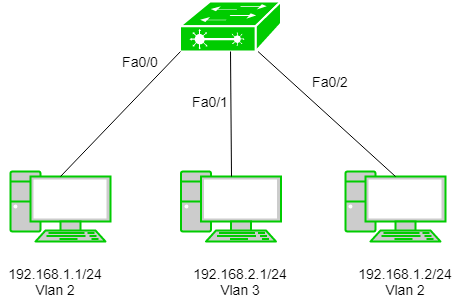
VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network A VLAN is a local area network where the computers, servers, and other network devices are logically connected regardless of their physical location. So, even if these devices are scattered in different places, it wouldn’t matter. Because a VLAN can logically group them into separate virtual networks. And the purpose of a VLAN is for improved security, traffic management, and to make a network simpler.So as an example, let’s say you have a three-story office building and in this building you have computers that belong to certain departments that are mixed in with computers that belong to other departments on the same floor. So, the red computers represent the accounting department The blue computers represent the shipping department; and the green computers represent the support department. Now as you can see, all these computers from these different departments are all connected to a switch. So, they are all on one segment on a local area network or LAN. So, all the network broadcast traffic are mixed in with other departments. So, the departments are all seeing each other’s network traffic. Now suppose as a network administrator You wanted to separate the network broadcast traffic from these departments from each other, so that the accounting department doesn’t see any traffic from support, support doesn’t see any traffic from shipping and so on. Now one way to solve this is to physically move the computers that belong to the same department and put them together such as putting them on the same floor and deploying extra network hardware and cabling. But, that could be a hassle and unnecessary work. But there is an easier way to accomplish this and that is by creating VLANs. By using VLANs on a VLAN capable switch you can logically create several virtual networks to separate network broadcast traffic. So, in this case, we’re going to create three VLANs for the three different departments. So, we’re going to create a VLAN for the accounting department and then we’ll create another VLAN for the support department And then we’ll create one for the shipping department. So now as the VLANs are implemented the traffic between the three departments are isolated. So they won’t see any traffic created from the other departments.They will only see their own network traffic even though all the computers from the different departments share the same cabling and switch So in our example the VLANs were created on the switch and this is done by designating specific ports on the switch and assigning those ports to a specific VLAN.So on the switch will create a VLAN for the support department.So we’ll plug all the computers that belong to the support department into those ports.Then we’ll designate another set of ports on the switch and create another VLAN for the accounting department.And finally, we’ll designate another set of ports on the switch for another VLAN for the shipping department.And, as you can see the network traffic is separated between the departments because of the VLANs.So, as stated before there are several different reasons for creating VLANs.But one of the main reasons is for traffic management because as a local area network grows and more network devices are added, the frequency of the broadcasts will also increase and the network will get heavily congested with data. But, by creating VLANs, which divide up the network into smaller broadcast domains, it will help alleviate the broadcast traffic.